
Are you a Human Resources Manager tasked with implementing layoffs for Filipino employees within a tight deadline? This article is your go-to guide! We’ll walk you through Philippine labor laws and personnel systems, ensuring you conduct layoffs legally, fairly, and efficiently. With practical advice, humor, and case studies, we’ll make the process both informative and engaging. Let us help you navigate this challenge with confidence and ease.
Overview of Philippine Labor Laws
Philippine labor laws serve as the cornerstone of the employer-employee relationship, encompassing various employment facets within the country’s jurisdiction. Applicable to all enterprises, joint ventures, and engagements with Filipino citizens and foreign firms, these laws ensure a fair and transparent work environment.
Here are the key highlights of Philippine labor laws:
Employment Types: The Philippines recognizes five employment categories, each carrying distinct rights and obligations, including probationary periods, overtime pay, and benefits.
Working Hours: Mandating an 8-hour workday or a 48-hour workweek, with mandatory rest periods after every 6 days, employees working beyond stipulated hours are entitled to overtime pay.
Minimum Wage: Varied by region and industry, the minimum wage standard for non-agricultural sectors in the Greater Manila Area is 537 pesos. Wages are to be disbursed bi-weekly and not in vouchers or tokens.
Holidays: Designating statutory holidays such as New Year’s Day, Labor Day, and Independence Day, employees with at least one year of service are entitled to five days of paid annual leave. Additionally, female employees enjoy up to 105 days of full paid maternity leave per pregnancy.
Termination and Redundancy: Termination is strictly governed by proper procedures and just or authorized causes, encompassing serious misconduct, fraud, and redundancy. Entitlements vary based on the cause of termination.
In addition to basic wages, employing workers in the Philippines incurs both statutory and non-statutory personnel costs, including income tax, social security, and health insurance. According to data from the Philippine and Fu Law Firm, employing a worker with a gross monthly salary of 18,000 pesos incurs approximately 28.6% in statutory benefits costs and around 7.7% in non-statutory benefits costs, totaling an additional 36.3% in personnel expenses outside the basic wage.
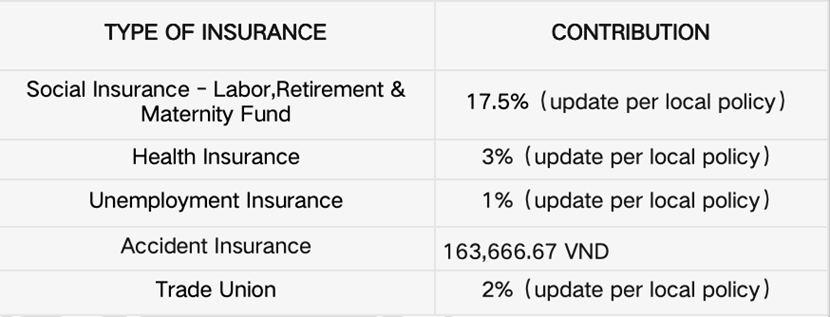
Employer contribution in Vietnam:
Layoff Strategies in the Philippines
It’s essential to have employment contracts that clearly outline job roles, responsibilities, and termination conditions. This clarity helps prevent misunderstandings and disputes later on.
For instance, a foreign company hired a sales manager in the Philippines with clear performance targets outlined in the employment contract. When the manager failed to meet these targets during the probationary period, the company was able to terminate the manager with ease, as the conditions for termination were clearly defined from the outset.
Conducting regular performance assessments allows employers to address issues of poor performance promptly. It’s crucial to document these assessments and provide employees with feedback to give them an opportunity to improve.
For example, a hotel in the Philippines provided verbal and written warnings to a front desk officer who repeatedly made mistakes. Despite counseling and training sessions, the officer’s performance did not improve, leading to termination for gross negligence.
Philippine labor law mandates that employees must be provided with written notices and a rebuttal period before termination. This ensures that employees have the opportunity to respond to the reasons for termination.
In a case where a garment factory laid off workers due to financial constraints, written notices were issued to all employees, providing them with a month’s notice and allowing them to respond. This adherence to due process helped avoid legal complications.
Employers in the Philippines are required to provide severance pay and termination certificates to employees terminated for authorized reasons. This helps ensure that employees are fairly compensated and have documentation of their employment status.
For instance, when a call center closed down operations, the company followed proper procedures by issuing written notices, paying severance based on years of service, and providing closure certificates to all employees affected by the closure.
Layoffs can be emotionally challenging for employees, and it’s important for employers to handle these situations with sensitivity, especially in the Philippines where people value respect and empathy.
In an example involving a restaurant terminating a chef for misconduct, the company provided additional support such as career guidance and consolation money, recognizing the chef’s personal challenges and mitigating potential resentment or conflict. This approach helped preserve the company’s reputation and maintain positive relations with the community.
Warning:Case Study: Illegal Layoffs Leading to Legal Proceedings in the Philippines
Scenario: A foreign-owned company established a manufacturing plant in the Philippines. Due to declining market demand and financial difficulties, the company decided to downsize its workforce to reduce costs. However, the company proceeded with layoffs without adhering to the proper procedures outlined in Philippine labor laws, lacking transparency and legality.
Illegal Actions:
Lack of Justifiable Reasons: The company failed to provide sufficient reasons to support its decision for layoffs, without conducting appropriate performance evaluations or warning procedures.
Violation of Legal Procedures: The company did not provide written notices or a rebuttal period to employees, proceeding with layoffs without following the statutory process.
Refusal to Provide Compensation: Due to illegal layoffs, the company refused to provide employees with the compensation and benefits they were entitled to.
Lack of Documentation: The company did not maintain detailed records related to layoffs, including notifications, performance evaluations, compensation payments, etc.
Consequences: As a result of the company’s illegal actions, employees initiated legal proceedings, accusing the company of unlawful terminations and refusal to provide compensation. The court ruled that the company must pay significant compensation, including severance pay, damages for illegal actions, and legal fees. The total compensation awarded amounted to approximately $100,000, including $80,000 in severance pay and $20,000 in damages and legal fees. Additionally, the company’s reputation suffered, leading to negative public perception and loss of clients.
Admonitory Role: This case serves as a clear warning to companies, emphasizing the importance of compliance with Philippine labor laws. Companies should strictly adhere to the layoff procedures, including providing justifiable reasons, written notifications, rebuttal periods, and proper compensation. Failure to do so may result in severe legal consequences, including substantial compensation payments and reputational damage, causing irreparable losses to the company. Therefore, companies should follow legal regulations during the layoff process to ensure legality, fairness, and protection of employees’ rights.
Discover Gonex EOR Services, your gateway to streamlined overseas business expansion and global workforce management. With expertise in navigating complex employment landscapes, interpreting policies, and managing payroll, we ensure compliance and efficiency. Our AI-driven solutions simplify payments, reduce risks, and ensure global compliance, giving your enterprise a competitive edge. Experience seamless onboarding, unified payments, and meticulous offboarding with Gonex. Choose sustainability, choose efficiency, choose Gonex EOR Services for your global expansion needs.Let Gonex assist you and your company with handling such complex overseas hiring processes!
To access more information on corporate international expansion cases, global employment guidelines, worldwide compensation management, regulations for various regional countries, and factory establishment manuals in different nations, you are welcome to visit the GONEX official website at www.letsgonex.com to download these resources or view our company’s business introduction in PDF format (https://letsgonex.com/in.pdf?from=inmail).